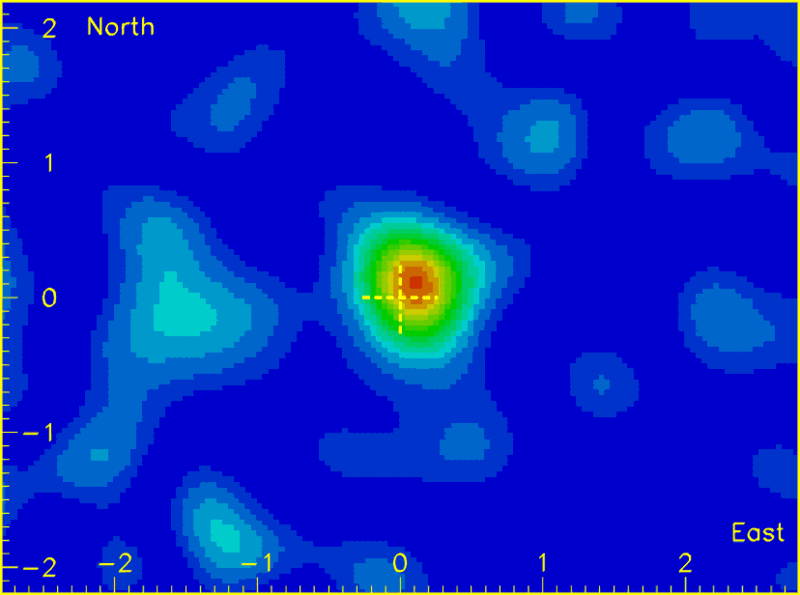
Soudan 2 is a subterranean detector located at a depth of 700 m in the Soudan Mine in Minnesota (USA) and was designed to look for nucleon decay. The basis of the study relates to the way in which the Moon blocks the arrival of cosmic rays into the Earth's atmosphere coming from its direction.
The shadow is the result of approximately 120 muons missing from a total of 33 million detected in Soudan 2 over its 10 years of operation. The yellow cross denotes the actual location of the moon.
Although the angular size of the Moon in the sky is relatively small, the effect on the detection of cosmic muons, carried out by the detector, can be seen as the shadow of the Moon. Since it is a moving body, the shadow was detected and observed over time.
The collected data confirmed the excellent capabilities of Soudan 2 in the execution of this work and as a detector of possible point astrophysical sources through the detection of muons.
Publication:
"Observation of a shadow of the Moon in the underground muon flux in the Soudan 2 detector" (Cobb et al. 1999)